
Past success
As the flies’ host and geographic range expand, pressure is intensifying to control the flies—something many countries have managed to do in the past.
Decades ago, screwworms were endemic throughout Central America and the southern US. However, governments across the regions used intensive, coordinated control efforts to push the flies southward. Screwworms were eliminated from the US around 1966, and were pushed downward through Mexico in the 1970s and 1980s. They were eventually declared eliminated from Panama in 2006, with the population held at bay by a biological barrier at the Darién Gap, at the border of Panama and Colombia. However, in 2022, the barrier was breached, and the flies began advancing northward, primarily through unmonitored livestock movements. The latest surveillance suggests the flies are now about 370 miles south of Texas.
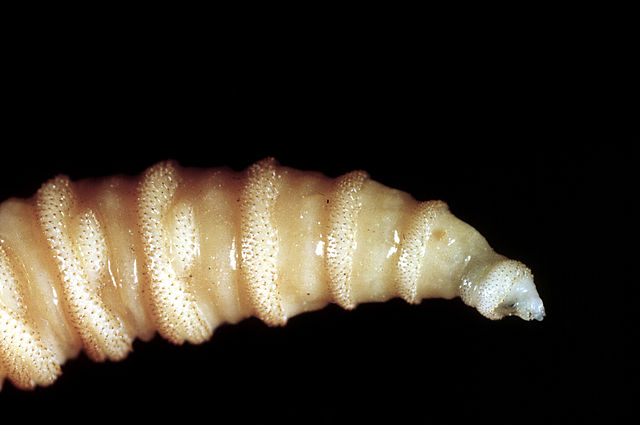
The main method to wipe out screwworms is the sterile insect technique (SIT), which exploits a weakness in the fly’s life cycle since they tend to only mate once. In the 1950s, researchers at the US Department of Agriculture figured out they could use gamma radiation to sterilize male flies without affecting their ability to find mates. They then bred massive amounts of male flies, sterilized them, and carpet-bombed infested areas with aerial releases, which tanked the population.
Panama, in partnership with the US, maintained the biological barrier at the Colombian border with continual sterile-fly bombings for years. But as the flies approached this year, the USDA shifted its aerial deliveries to Mexico. In June, the USDA announced plans to set up a new sterile fly facility in Texas for aerial deliveries to northern Mexico. And last month, the USDA halted livestock trade from southern entry points.
Miller said in the announcement today that SIT is no longer enough, and Texas is taking its own steps. Those include the new bait, insecticides, and new feed for livestock and deer laced with the anti-parasitic drug ivermectin. Miller also said that the state aims to develop a vaccine for cattle that could kill larvae, but such a shot is still in development.













Leave a Reply