
This article originally appeared on Inside Climate News, a nonprofit, non-partisan news organization that covers climate, energy, and the environment. Sign up for their newsletter here.
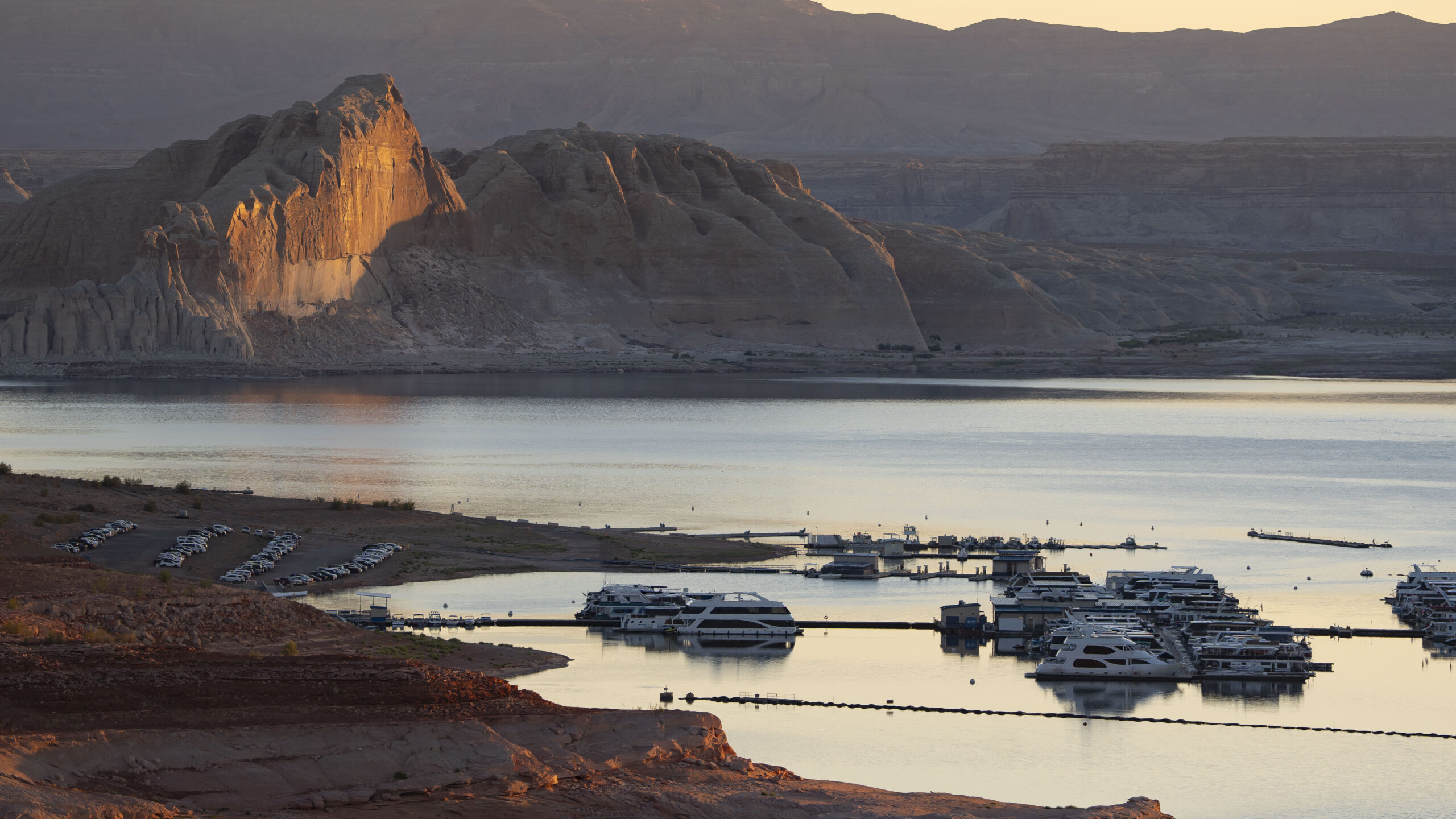
The drought in the Southwestern US is likely to last for the rest of the 21st century and potentially beyond as global warming shifts the distribution of heat in the Pacific Ocean, according to a study published last week led by researchers at the University of Texas at Austin.
Using sediment cores collected in the Rocky Mountains, paleoclimatology records and climate models, the researchers found warming driven by greenhouse gas emissions can alter patterns of atmospheric and marine heat in the North Pacific Ocean in a way resembling what’s known as the negative phase of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO), fluctuations in sea surface temperatures that result in decreased winter precipitation in the American Southwest. But in this case, the phenomenon can last far longer than the usual 30-year cycle of the PDO.
“If the sea surface temperature patterns in the North Pacific were just the result of processes related to stochastic [random] variability in the past decade or two, we would have just been extremely unlucky, like a really bad roll of the dice,” said Victoria Todd, the lead author of the study and a PhD student in geosciences at University of Texas at Austin. “But if, as we hypothesize, this is a forced change in the sea surface temperatures in the North Pacific, this will be sustained into the future, and we need to start looking at this as a shift, instead of just the result of bad luck.”
Currently, the Southwestern US is experiencing a megadrought resulting in the aridification of the landscape, a decades-long drying of the region brought on by climate change and the overconsumption of the region’s water. That’s led to major rivers and their basins, such as the Colorado and Rio Grande rivers, seeing reduced flows and a decline of the water stored in underground aquifers, which is forcing states and communities to reckon with a sharply reduced water supply. Farmers have cut back on the amount of water they use. Cities are searching for new water supplies. And states, tribes, and federal agencies are engaging in tense negotiations over how to manage declining resources like the Colorado River going forward.














Leave a Reply